 buttons opens the Speaker Processing window.
buttons opens the Speaker Processing window.The exact look of the panel will vary if the device is being individually controlled or in a Master Panel. This variance also includes the controls that are included on the Master Panel.
Double clicking on the  buttons opens the Speaker Processing window.
buttons opens the Speaker Processing window.
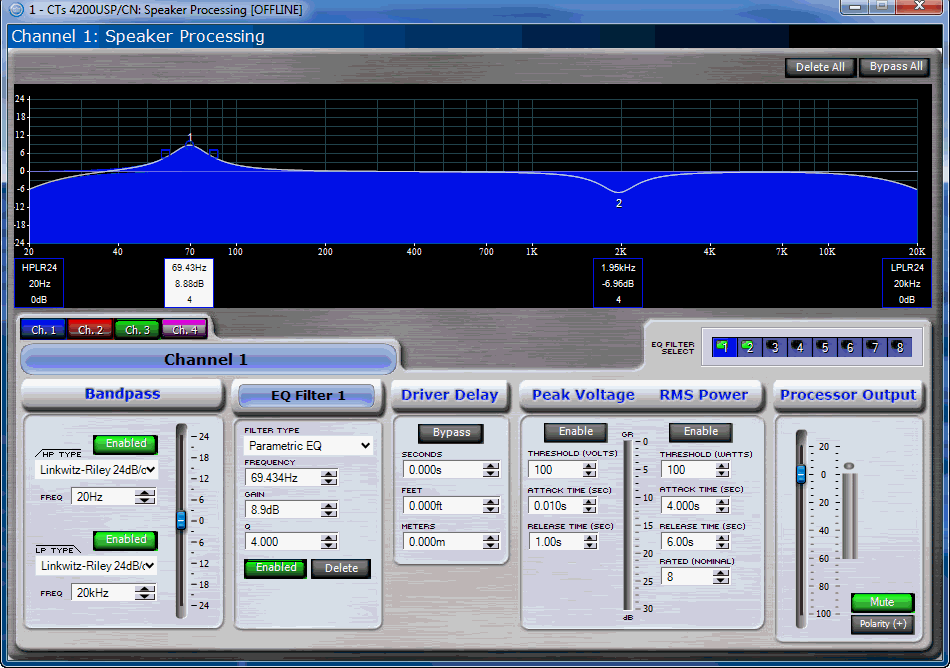
The Speaker Processing Block provides controls that are grouped to provide processing and protection for a speaker. This control screen provides the most commonly used controls in a format that allows for quick adjustment and the ability to see the settings of the system at a glance.
The settings can be grouped into four distinct control types:
There are two band pass filters available within the module. There are no functional differences between the high and low pass filters.
The frequency control allows one to select the 3dB for the filter, often called the knee of the filter. You can either adjust the frequency by using the control on the graph or using the numeric spin control.
The drop down box for the filter type allows one to select the filter slope and style. The options are:
Butterworth 6dB/octave
Butterworth 12dB/octave
Butterworth 18dB/octave
Butterworth 24dB/octave
Bessel 12dB/octave
Bessel 18dB/octave
Bessel 24dB/octave
Linkwitz-Riley 24dB/octave
This button activates or deactivates the filter.
The input filter controls allow for multiple ways to enter data as well as view the information quickly. The controls are:
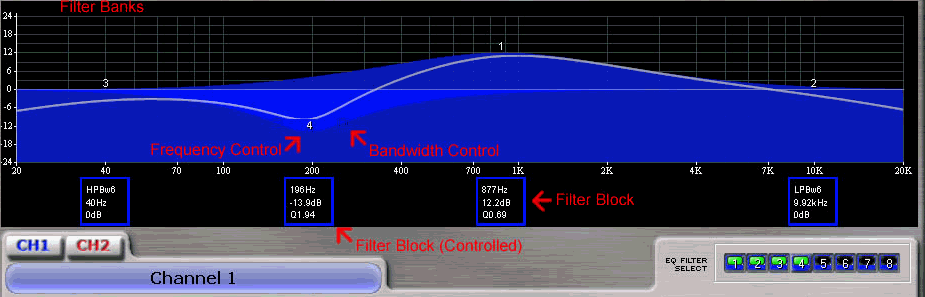
Filter Bank Selection
Flat
Restore
Bypass
Filter Block
Frequency Control
Bandwidth Control
Filter Used/Selected
Filter Enabled
In addition to these controls, the graphic view allows for one to change the parameters quickly and easily.
The Flat button will return all of the filters in the bank to its default values.
The Restore button will return the values of all filters to the last settings before activation of the Flat button. If a user has made a change to the filters, it will return the values to the settings before the Flat button was pressed. This action will result in the loss of any changes.
The Bypass button will disable all of the filters in that bank, delivering an unprocessed signal through the filter section.
The Filter Block provides a visual display of the values for the filters that are currently active in the processing section. The filter currently selected for editing will be highlighted in White. The information shown will vary depending on the filter type. If the filter is a Parametric Filter, the block will display Center Frequency, Gain, and Width. If the filter is not parametric, the block will display the Filter Type, Frequency, and Gain.
You can adjust the center frequency of the filter by moving the Filter Block horizontally.
The Frequency Control on the graph allows you to adjust both the center frequency and amount of gain. To adjust the gain, move the control vertically; move the control horizontally to change the center frequency. Clicking on the frequency control will bring that filter under control for editing.
The square control points allow you to graphically adjust the width of the filter. These controls are not shown when the filter is not under control to reduce clutter on the screen.
The Filter Used/Selected squares display the status of filters being used. If a filter is used but not active, its corresponding square will be yellow. If the filter is active, the square will be green. If the filter is unused the square will be gray. Clicking on the filter square will also bring control to that filter.
The Filter Enable button allows you to individually engage or bypass a filter. The square is green when the filter is engaged; it is gray when it is bypassed.
The Delay Block contains a signal delay display. You may enter the delay in either milliseconds, feet, or meters.
Note: Delays added through the delay block are in addition to any latency delay that may already be occurring as the result of a variety of factors. Fixed latency delays are always present in the module itself:
DSP Processing: 32 bit, Floating Point, 665 µs latency.
DAC Conversion: 24 bit, 135 µs latency.
ADC Conversion: 18 bit, 312 µs latency.
There is a separate delay for the input processing section. It is typical to use the Input Delay to compensate for distance from a point source and to use the Output Delay for driver to driver alignment.
The Output Limiter Section allows you to keep the amplifier in a safe power range for the speaker. The controls available are:
The Peak Voltage Limiter block provides controls allowing you to limit the peak voltage of the output signal through the amplifier. Each Peak Voltage Limiter section includes:
Click on this button to turn the Peak Voltage Limiter on and off.
Use this control to set a peak voltage in volts.
Use this control to set the amount of time after the voltage threshold is exceeded before limiting takes place. The range for this control is 10 to 100 milliseconds
Use this control to set the amount of time after the voltage drops below threshold before limiting will be released. The range for this control is 0.1 to 10 seconds
The RMS Power Limiter block provides controls allowing you to base limiting on the RMS (Root Mean Square) power of the output signal through the amplifier. The RMS Power Limiter section includes four controls:
Click on this button to turn the RMS Power Limiter on and off.
Use this control to set a maximum RMS power in watts. The range for this control is 10 to 10,000 watts.
Use this control to set the amount of time after the RMS power threshold is exceeded before limiting takes place. This control has a range of 1 to 30 seconds
Use this control to set the amount of time after the RMS power drops below threshold before limiting will be released. The range of control is 1 to 30 seconds.
Use this control to enter the nominal impedance for the load attached to the amplifier. This value helps the device provide a more accurate reading by properly weighting the values the amplifier is reporting and the device is making the calculations from.
The output level control allows for you to control the amount of gain that is applied post equalization in the Speaker Processing Block. This control is recommended to be used for adjusting the level between different drivers in a multiway speaker system.